By 2025, 90% of new data and analytics deployments will be through an established data ecosystem, causing consolidation across the data and analytics market and 55% of IT will adopt data ecosystems, consolidating the vendor landscape by 40%, thereby reducing cost while reducing choice.
By 2027, 75% of DBMS purchases will be made by line-of-business domain leaders, up from 55% in 2022. During the same timeframe, the IaaS and PaaS spending would triple, thereby driving the demand for Database Platform as a Service or dbPaaS. Also, by 2027, Relational Database Management Systems or RDBMS offerings will feature 80% of the practical functionality of their NoSQL competitors, up from 60% in 2022.
In the recent 2023 Magic Quadrant for Cloud Database Management Systems (DBMS), Gartner recognized AWS as a Leader and positioned it highest in the Ability to Execute among all the vendors evaluated.
What is the Market for Cloud Database Management Systems?
Gartner defines the market for cloud DBMSs as the market for software products that store and manipulate data and that are primarily delivered as SaaS in the cloud. The Cloud DBMSs may be capable of running on-premises or in varied environments like hybrid, multi-cloud, or inter-cloud configurations, but that is optional. They may be used for transactional work and/or analytical work. They may be equipped to participate in a wider data ecosystem.
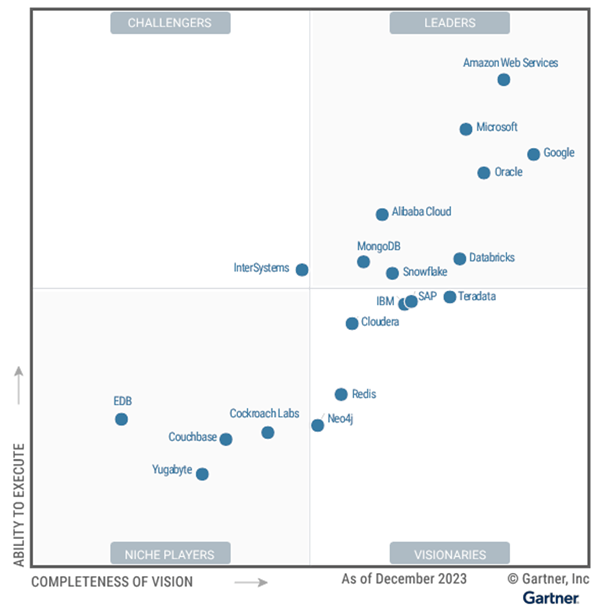
Source: Gartner
What do Cloud DBMSs do?
Cloud DBMSs enable organizations to execute their optimization strategies to support transactional and/or analytical processing for different use cases, such as:
Online Transaction Processing Transactions
- Centralized transaction focus
- Fixed and stable schema
- High-speed, high-volume
- Concurrency and data insert/update capabilities
- Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID)
Lightweight Transactions
- High-volume simple transactions
- High-concurrency
- Relaxed consistency
- May involve processing fast-moving events captured from the edge
Operational Intelligence
- Several concurrent users running short analytic queries
- Focused on meeting appropriate performance SLAs
- Relates to transactional databases that perform predictive model execution & OLAP
- Relates to analytical databases supporting several users running highly concurrent workloads of simple queries
Traditional Data Warehouse
- Managing structural historical data from varied sources in one DBMS instance
- Data structuring to enable flexibility
- Supports high-performance
Logical Data Warehouse
- Managing variety and volume of structured data as well as other types of data
- Acting as a logical tier for different internal and external data sources
- Involves analytics across the data ecosystem
Data Lake and Machine Learning
- Involves storage & processing of different structural data
- Includes data engineering, data science, and other use cases at scale
These are the different use cases for players in the market as Gartner defines it. Based on this, Amazon Web Services has been ranked as a leader, which is a commendable achievement for the platform.
Amazon Web Services offers a comprehensive suite of database services with purpose-built engines to support operational, transactional, analytical, and streaming applications. AWS offers an extensive selection of database services that support a diverse range of customer needs, including both highly specialized demands as well as varied use cases, in turn helping bring scalability, flexibility, and many other attributes to enterprises of all sizes.
Amazon Web Services is the world’s largest cloud service provider and holds the highest market share globally. It has dedicated teams and service delivery partners that make the experience of migrating one’s databases to AWS very easy, simple, and efficient. With AWS one also gets extended AWS-based solutions with continuous improvements as well as encourages innovation, enabling users to get what they most desire – scale, latency, security, compliance, as well as important integrations.
What are the key strengths of AWS as a Cloud Database Management System?
There are key strengths that make AWS stand apart as a cloud database management system. These are:
-
Market Leader Presence:
Amazon Web Services has a very strong global presence. It was the first mover in the space and has held the position of the market leader forever. It has extensive offerings and best-in-class services along with a very strong partner community and, a wide library of third-party tools and services, all of which help Amazon Web Services deliver complete, compliant, as well as secured database applications to enterprises of all sizes anywhere in the world.
-
Database Engine & Model Flexibility:
Amazon Web Services offers purpose-built database engines that are incredible in supporting different data models – relational, document, in-memory, key-value, graph time series, wide column, and ledger databases. This gives users much-desired flexibility as well as interoperability, so one can choose whatever database would best fit the application they are building.
-
Extensive Data Ecosystem Integrations:
With Amazon DataZone, Amazon built a common metadata framework, to offer users an efficient integration between services. With work going further in this direction, AWS is best placed to enable users to build a more integrated set of solutions.
Today, 76 of the Fortune 100 companies use IBM Db2 databases, according to Amazon Web Services. It gives Db 2 customers an additional option to remove undifferentiated database management risks while also enabling them to achieve high availability as well as cloud agility.
Amazon Web Services now also offers a full range of vector search capabilities and tools with Amazon OpenSearch Service, Amazon Aurora, and Amazon Relational Database Service. Vector engines will be generally available for Amazon OpenSearch Serverless while vector search will be available for Amazon DocumentDB as well as Amazon Neptune. Amazon DynamoDB users can also perform near real-time vector searches using zero-ETL integration with the Amazon OpenSearch Service.
Amazon is also working full-throttle in harnessing the power of Generative AI to power its data services across the board.

Get AWS Certified to Future-Proof Your Career
As businesses undergo digital transformation, their consumption of IT systems and services undergoes a parallel evolution. Simultaneously, major cloud providers release a staggering array of features and services every year, a pace that far surpasses the traditional hardware development cycles of the past.
Those entrusted with the responsibility of architecting solutions in this dynamic environment must continually adapt and equip themselves with the skills needed to thrive in this new landscape. The role of an AWS Solutions Architect has undeniably evolved over the years, shaped by the forces of technological innovation and the demands of the cloud-native era.
Embracing this evolution and remaining well-versed in the ever-changing AWS ecosystem is essential for architects tasked with designing solutions that meet the evolving needs of businesses in the modern IT landscape. By doing so, AWS Solutions Architects can navigate the complexities of this transformative journey and continue to deliver value in an industry defined by perpetual change and innovation.
Enroll in Cognixia’s cloud computing with Amazon Web Services training course and upgrade your skill set. You can influence your career and future with our hands-on, live, highly interactive, and instructor-led online course. You may benefit in this competitive market by providing an extremely user-friendly online learning experience. We will assist you in improving your knowledge and adding value to your talents by offering engaging training sessions.
Cognixia’s AWS cloud computing certification course discusses the basics of AWS & cloud computing, then moves on to more advanced concepts, like service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), Amazon Private Virtual Cloud (AWS VPC), and more.
This online AWS cloud computing course will cover the following concepts:
- Introduction to AWS & Cloud Computing
- EC2 Compute Service
- AWS Cost Controlling Strategies
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, i.e., VPC
- S3 – Simple Storage Service
- Glacier
- Elastic File System
- Identity Access Management (IAM)
- ELB (Elastic Load Balancer)
- Auto Scaling
- Route53
- Cloud Formation & Cloud Former
- Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- CloudWatch
- Relational Database Service (RDS)
- CloudFront
- Elastic Beanstalk
- CloudTrail
- AWS Application Services for Certifications
Prerequisites AWS cloud computing certification course
All you need to know to enroll in this course is basic computer skills. Some experience with Linux would be advantageous, but it is not required.
The course is perfect for network engineers, system administrators, and aspirants who have a solid understanding of coding principles or procedures and wish to further their expertise.

