Extensive automation, complete monitoring, seamless collaboration, and increased productivity – these are the requisites of a perfect software development endeavor that delivers the best products and services in the minimum time.
The software development industry had a long cherished dream of achieving this perfection one day. The traditional approaches were good and lasted for decades, each contributing to the improvement of the overall process with time. And today, in the era of industry 4.0, we have DevOps at our disposal. DevOps has brought us quite near to achieve the excellence in developing software that every IT professional had at least once dreamt of, by overcoming the challenges that plagued the prior approaches.
“Many organizations are in the experimentation stage but they all are transitioning towards DevOps entirely.”
—Forrester
Software Development Challenges
The traditional approach of software development faces several challenges:
From the developers’ perspective, the code deployment time was unnecessarily large even after successful development. Also, the burden of working on the pending code and new code was consistently huge, causing a feeling of anxiety among the developers.
The operations team, on the other hand, faced the difficulty to maintain near about 100% production environment uptime. As development continued, the number of servers kept increasing and monitoring them became more complicated and time-consuming. In addition, the automation tools for the infrastructure were not very effective, and thus diagnosing issues in the product was extremely difficult. Naturally, providing feedback on the product also became difficult.
DevOps Solutions
DevOps utilizes continuous integration to ensure that the code deployment is quick, testing is agile, and feedback mechanisms are speedy. Thus, the challenge of huge waiting time for code deployment is overcome, and developers can now focus on working and developing the current code. There is no more anxiety of working on the new code and the old code at the same time.
DevOps introduces the concepts of virtualization and containerization that creates simulated environments to run the software as containers. This is a reliable way of ensuring service uptime. Thus, the difficulty to maintain the production environment uptime vexing the operations team is overcome.
There is another concept of configuration management in DevOps that organizes configuration plans and executes them appropriately. This ensures the provisioning of the system in a consistent manner and proactive management of the overall infrastructure. This way the dearth of effective automated infrastructure tools is, therefore, eliminated for the operations team.
DevOps uses an open-source monitoring application called Nagios for effective and continuous monitoring. Due to this application, there is no overhead on the operations team as there is no overwhelming increase in the numbers of servers to be monitored. There is, therefore, no difficulty in diagnosing and providing feedback on the products and services.
Although the discussion until here has focused on the challenges faced, and the solutions provided by DevOps to the development and operations team separately. In essence, this is achieved by breaking the silos between the development and operations team. Thus, it is appropriate to think of DevOps as a collaboration of the two teams into one entity.
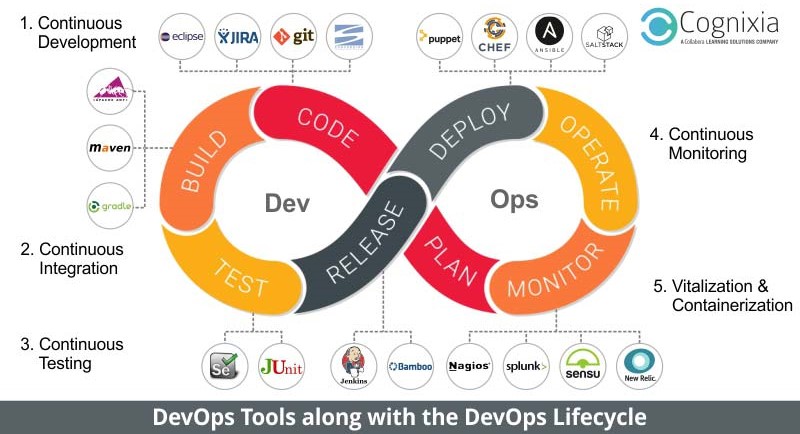
DevOps Lifecycle
The DevOps lifecycle along with the most preferred tools are –
-
Continuous Development
This phase covers planning and coding. Sometimes, this phase is broken down into two steps, one – the planning phase in which the objective of the project is decided and two, the coding phase in which the code is to be written.
Popular Tools: GIT, JIRA, Mercurial, CVS -
Continuous Testing
Bugs must be eliminated from the code before releasing it. Also, the performance of the application must be fine-tuned. This stage achieves that.
Popular Tools: Selenium, JUnit/NUnit, TestNG -
Continuous Integration
This phase and the tools used in it hold together the entire DevOps structure. CI tools can be integrated with the tools in all the other stages of the DevOps lifecycle.
Popular Tools: Jenkins, Hudson, Bamboo -
Continuous Deployment
This is the phase of real action. Configuration Management and Containerization tools are used here and they help in achieving seamless deployment.
Popular Tools for Configuration Management: Ansible, Puppet, Chef, SaltStack
Popular Tools for Containerization: Docker, Vagrant -
Continuous Monitoring
Bugs often go undetected in the testing phase. This is the universal truth about the software development galaxy. Monitoring helps in finding these bugs, and leaving no stones unturned when it comes to performance tuning.
Popular Tools: Splunk, Nagios
If this brief discourse on DevOps has inspired you to learn it, Cognixia can be your one-stop learning partner. We are an e-learning and digital transformation preceptor, with a wide-range of courses on DevOps for students, professionals, and corporate workforce. Reach out to us for more information at join@cognixia.com

 Workforce Transformation Consulting
Workforce Transformation Consulting

